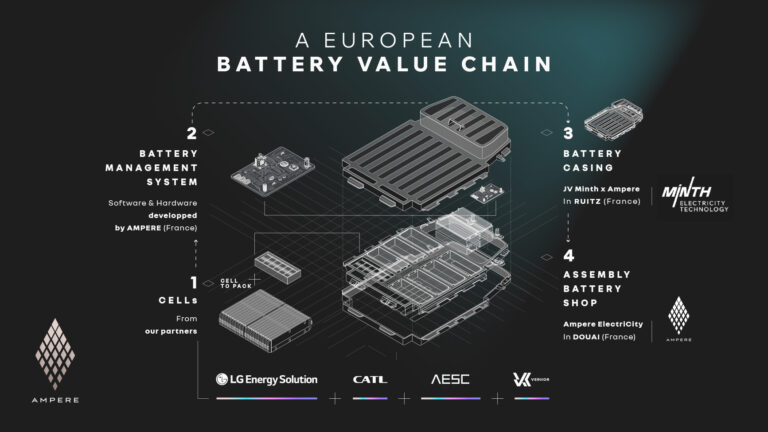
Ampere, Renault’s European electric vehicle (EV) subsidiary, has shared an ambitious new battery strategy that incorporates lithium iron phosphate (LFP) technology alongside the existing nickel cobalt manganese (NCM) batteries used by Renault Group.
LFP is less energy-intensive than NCM, making it a cost-effective and viable alternative. The company says this technology is crucial for making EVs more affordable and accessible in Europe.
Ampere’s is also collaborating with battery company LG Energy Solution (LGES) to introduce cell-to-pack (CTP) technology for pouch-type batteries. This technology is enables more cells to be packed into a given space, thus improving range and reducing costs.
“The work we’ve done with LG Energy Solution has enabled us to localize the entire value chain around LFP technology in Europe, and significantly increase its competitiveness, including with ‘cell-to-pack’. Innovation in batteries is ongoing, and we are working far upstream – in particular with our Innovation Battery Cell Laboratory to open in Lardy in 2025 – to engage our partners early on with us, on the major transformations to come,” said Philippe Brunet, SVP of powertrain and EV engineering at Ampere.
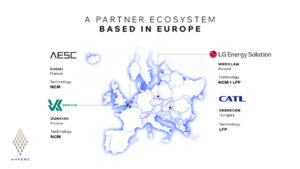
The battery plan includes setting up an integrated value chain in Europe. Partners such as LGES and Contemporary Amperex Technology (CATL) will provide LFP batteries for various models of Renault and Alpine brands, meeting battery needs until 2030.
“In a fast-changing and competitive environment, our battery strategy is proof of the efficiency of Ampere’s open and horizontal approach with best-in-class partners, ensuring smart capital allocation, flexibility and rapid execution. This plan is in line with Ampere roadmap to reduce costs by 40% before the next generation of vehicles,” said Josep Maria Recasens, COO of Ampere.
Ampere plans to install LFP technology in vehicles in record time, with the first models expected to be equipped by early 2026. As a result, the company suggests that the integration of LFP and CTP technologies is expected to lower battery costs by approximately 20% by the start of 2026.