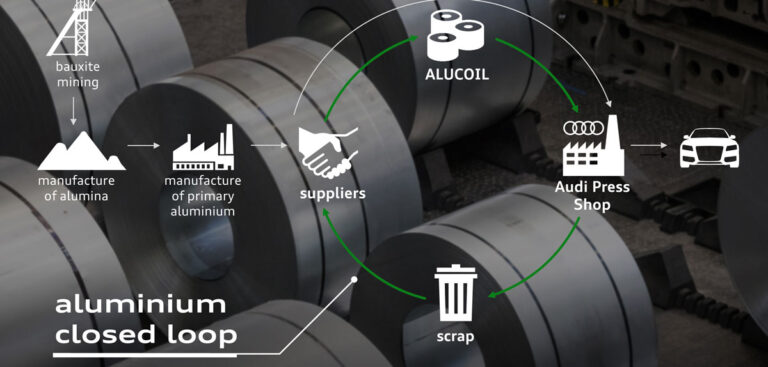
Audi’s CO2 reduction program has identified a 1.2-ton CO2 reduction potential per car. Due to range electrification, a large proportion of CO2 emissions come from the supply chain and in upstream production processes.
As such, Audi is developing measures to reduce emissions from that phase. The focus of the CO2 program is on particularly energy-intensive materials used in production, such as aluminum, steel and battery components.
In 30 workshops with suppliers, 50 measures have so far been developed with the potential to reduce CO2 per car by 1.2 tons. Specific potential for CO2 reductions exists in closed material cycles, successive increases in secondary materials, the use of recycled materials in plastic components and the use of green electricity.
For future orders, Audi intends to agree with its suppliers on the implementation of these measures, which are to be fully effective by 2025. The use of green power has been an integral element of supplier agreements with manufacturers of high-voltage battery cells since 2018.
Bernd Martens, board of management member for procurement and IT at Audi, said, “Already in the first year of the CO2 Program, we identified 50 concrete measures with our partners that contribute to the consistent decarbonization of our company. We are also creating more transparency in the supply chain.”
Audi plans to conduct further workshops next year in order to identify additional potential.