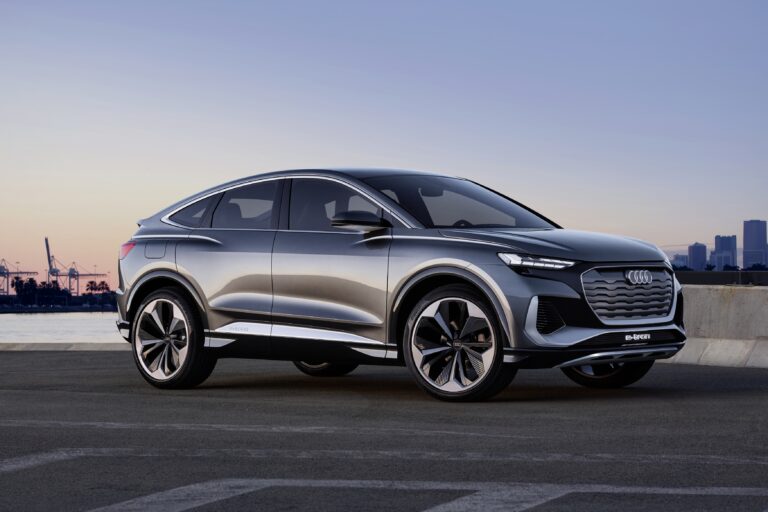
The mid-size e-SUV market looks to be heating up with Audi’s unveiling of its Q4 Sportback e-tron, a coupe version of the Q4 e-tron revealed in 2019, which is based on the VW Group’s MEB platform.
The Q4 will feature two drive motors, one front, one rear, with outputs of 150kW and 75kW respectively, which are fed by an 82kWh battery mounted in the floor. Audi stated that the charging system will be rated at 125KW, giving a 30-minute charge time to 80% capacity and a range in excess of 279 miles on the WLTP. The company noted that in day-to-day driving, the rear motor will provide the bulk of drive.
It is interesting that Audi has opted for a blend of motor types in the Q4. The rear motor is a permanent magnet unit, while the front is an asynchronous induction type. With the front motor only in use some of the time, an induction motor means there will be no associated losses due to magnets in the unused motor. Notably, Audi has used aluminum for the windings in it motors, which are produced at the company’s Győr facility in Hungary. The car is due to go on sale in 2021.
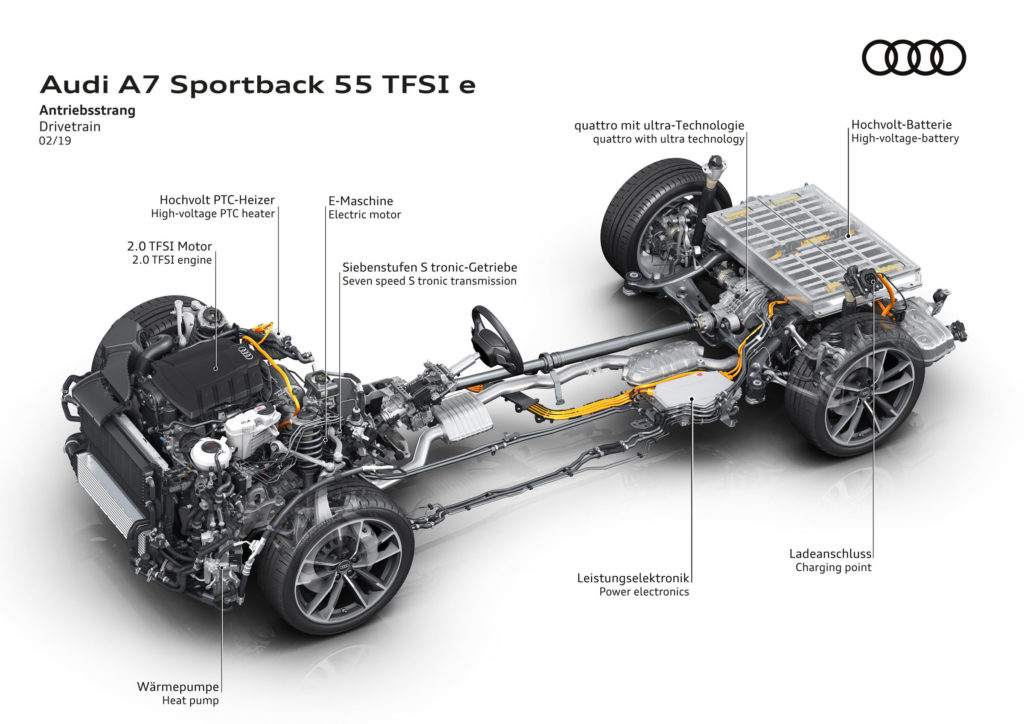
Though the pure EV models from Audi are currently stealing the limelight, the company also announced recently a plug-in hybrid version of the A7 (below). This combines a 2.0 liter, I4, TFSi engine with an electric motor mounted between the engine and 7-speed dual-clutch transmission. The combined output of the IC and EV elements is 362bhp.
Audi said the A7’s lithium-ion battery pack has a capacity of 14.1kWh and operates at 381V. To help bolster efficiency, the climate control system uses a heat pump that pools the waste heat from the high-voltage components and instead uses it to heat the vehicle’s cabin.